I first learned about Bitcoin in 2013 when I considered it as a payment method for my first e-commerce store. I never set it up… a huge mistake. I would have made more just doing that
Then in 2017, I (and everyone else) got into crypto during the last big bull run that saw Bitcoin reach 19k. Like many people, I was in it for the speculation and knew nothing about the technology behind it. I remember sitting on a beach in Thailand while some guy explained Ethereum smart contract technology.
I understood little of what he said, but I still bought some anyway.
My brain: “Hmmm number go up?”
My crypto assets at their high in 2017 were around 90k, and when the market crashed at its lowest they were 11k. Woof. (still HODL)
Over the last year, I’ve gone deep into crypto. Except this time learning and using it as a financial tool rather than mere speculating. A significant amount of my net worth is now in crypto as I believe it’ll play a huge role in the future.
This article is my attempt at writing an introduction to Decentralized Finance and why I find it so interesting.
This article is not financial advice. DeFi is the Wild West right now and comes with volatility and risk. This article is for informational purposes only.
Decentralized finance (DeFi), is the fusion of finance and blockchain technology.
It’s the movement to build a world where loans, interest rates, and an entire financial industry are controlled by individuals. A world where there’s no relationship between banks and money, no middlemen taking their cut – only individuals trading with each other.
Before I dive into DeFi let’s first talk about how this all works with blockchain technology.
What is a blockchain?
A blockchain is a digital public ledger.
Think of it like a public Google doc that everyone can see. They can see if there’s a change made, what it was, who changed it, and when they did it.
All that information is stored on a digital ledger. This ledger is duplicated and distributed across a network of thousands of computers on a blockchain.
These nodes are why the blockchain is “decentralized”. While I compared the Blockchain to a global Google doc, no one company (like Google), person or government owns it. Nor can they go in and delete or fudge any information.
Because of this, censorship or shutdown would be hugely complicated and an extremely difficult ordeal. This is why it’s considered so secure.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is money that uses cryptographic proof (the blockchain). Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency. It was designed to handle peer-to-peer payments without needing to involve intermediaries. Everything would be based on cryptographic proof rather than the blind trust that we give to banks.
Different cryptos are housed on different blockchains. (ADA is on the Cardano blockchain, Ether on Ethereum, etc)
That’s the most I’ll be talking about Bitcoin tho, as DeFi is built on Ethereum. Bitcoin’s little (and better IMO) brother and the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap. It was created by Vitalik Buterin (and team) and launched in 2015 after years in the making.
While Bitcoin is known for its peer-to-peer payment system, Ethereum is capable of more than transactions. It can power decentralized applications (like financial tools and social media platforms) using smart contract technology.
Here’s how I think about it:
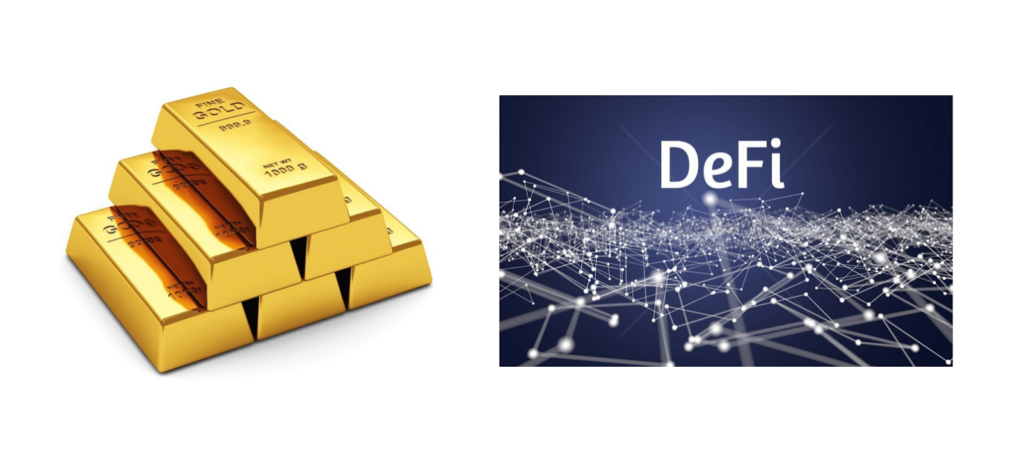

Bitcoin is digital gold, AKA A store of value.
Ethereum is the Internet, a platform of possibilities.
Ethereum is the platform on which apps (websites, businesses, apps) can be built on top of. We’ve already seen the explosion of NFTs using ERC721s tokens and this is only the beginning.
DeFi is the financial industry that is being built using Ethereum as a platform.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts help you exchange money, shares, or anything of value in a transparent, conflict-free way while avoiding the need for a middleman.
While blockchain acts like a database, confirming that transactions have taken place. Smart contracts execute predetermined conditions like executing on “if/then,” protocols.
So how might this look in real life?
Commercial real estate is ripe for disruption due to the length, complexity, and expense it takes. If all property details were stored on the blockchain (title, ownership history, etc) were stored on the blockchain, buyers and sellers could easily access that information. Instead of relying on title management companies and agents,
Commercial real estate transactions are often lengthy and complex endeavors. However, blockchain could make the process less burdensome.
If all property details, including key information about ownership history and titles, were stored on a blockchain, buyers and sellers could easily access it. You can do this with NFTs, seeing price history, ownership, etc — each house would be its own NFT for example.
Through smart contracts and the blockchain, the middlemen would be cut out as information could be verified faster. The transaction time, costs, and fees would decrease significantly as you wouldn’t need as many intermediaries.
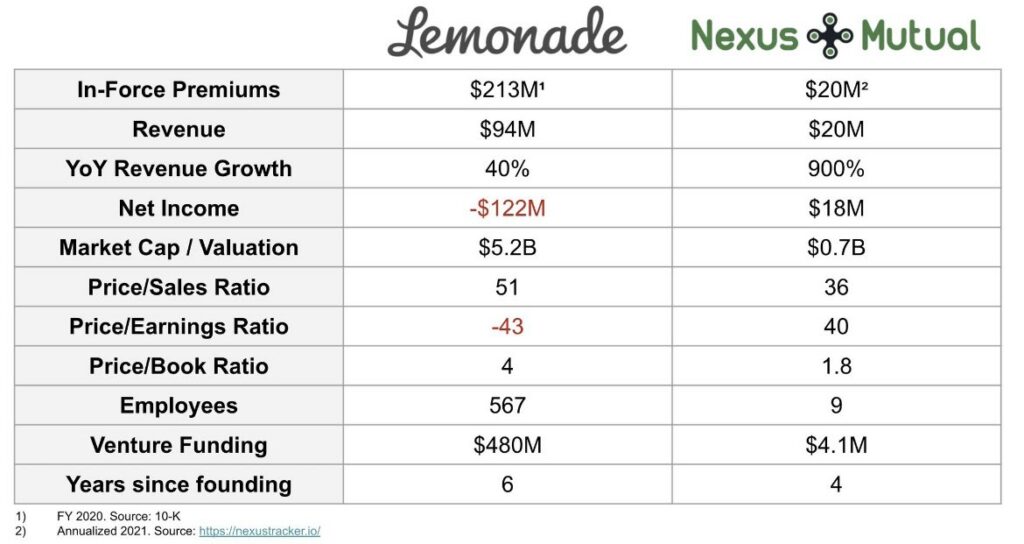
Another example is insurance, which compares the Fintech app Lemonade to that of DeFi protocol Nexus Mutual. Better at both scale and capital efficiency:
Another use case I thought about was concert tickets. Thread here:
⚡️NFT Concert Ticket Platform 🎫
When looking for @justinbieber tickets this weekend (yes I’m a Belieber) I had an idea for how to create a platform that’s better for the fans & the artists.
(and dis-incentivizes scalpers)
Here’s how it works:— Cathryn 🌈 (@cathrynlavery) June 1, 2021
DeFi Vs TradFi
Firstly, let’s go over how traditional finance works. When you bank with a company like Chase, Wells Fargo, or Bank of America (god forbid) you are allowing them to take your money and then decide what to do with it.
The bank will use that money for loans (like mortgages, auto loans, credit cards, etc) and whatever else they see fit. On average this is the type of return they see per different type of loan (roughly):
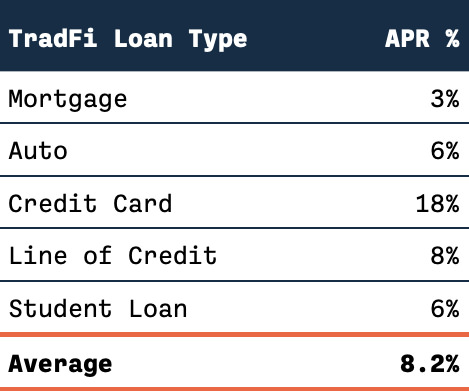
rough numbers on what a bank gets on your $$
The banks will make an average interest rate of 8.2% on the money.
Then they pay you 0.35% APR in a “high-yield savings” account or a whopping 0.02% in a standard checking account.
Given a 2% inflation rate, this means your money is losing value every day it sits in one of these “high-yield” accounts.
Banks also typically rely on a fractional reserve system where they lend out more money than they have on hand. They will lend up to 10X of their money in reserves, essentially creating a credit system. So for every $1 of your deposits, they might lend out $10.
(It’s one of the ways that we all got f**ked in 2008.)
Decentralized Finance is now removing the need for the “trusted” middleman through crypto & smart contract technology. With decentralized finance applications, we can connect lenders to borrowers through code — and cut out the bureaucratic middleman.
If you’ve ever tried to get a bank loan (or a mortgage), you know what a headache it can be with regulations, and paperwork and usually, it takes forever.
In crypto, it’s much simpler, requires no personal information (or credit score), and can be handled in minutes rather than months!
Now remember that 8% that the banks were getting on your money? You now can access this rate of return with relatively low risk.
TLDR:
Traditional finance: People are in charge of the system. They process transactions and write/maintain contracts. Due to human error/corruption, this can lead to problems
Decentralized Finance: No people are in charge of the system, the system manages itself. This is done through blockchain technology and computational contracts.
In DeFi we cut out the middlemen, the network keeps track of itself and everyone just uses it.
Stablecoins
Whenever I mention DeFi as a tool, often the first question I get back is regarding the volatility. Yes, I can maybe make 8% on my money but what if the asset drops 50% in value?
Good question. That’s where stablecoins come in. A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency whose value is tied to an outside asset, such as the U.S. dollar or gold, to stabilize the price.
For example in 2017 (the last crypto bull run), assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum were highly volatile and stablecoins weren’t a thing yet. So to hold value you’d have to transfer back to fiat currency or risk moving to another crypto asset which was also volatile.
Stablecoins make DeFi a much more valuable proposition for those scared of the volatility that crypto is famous for.
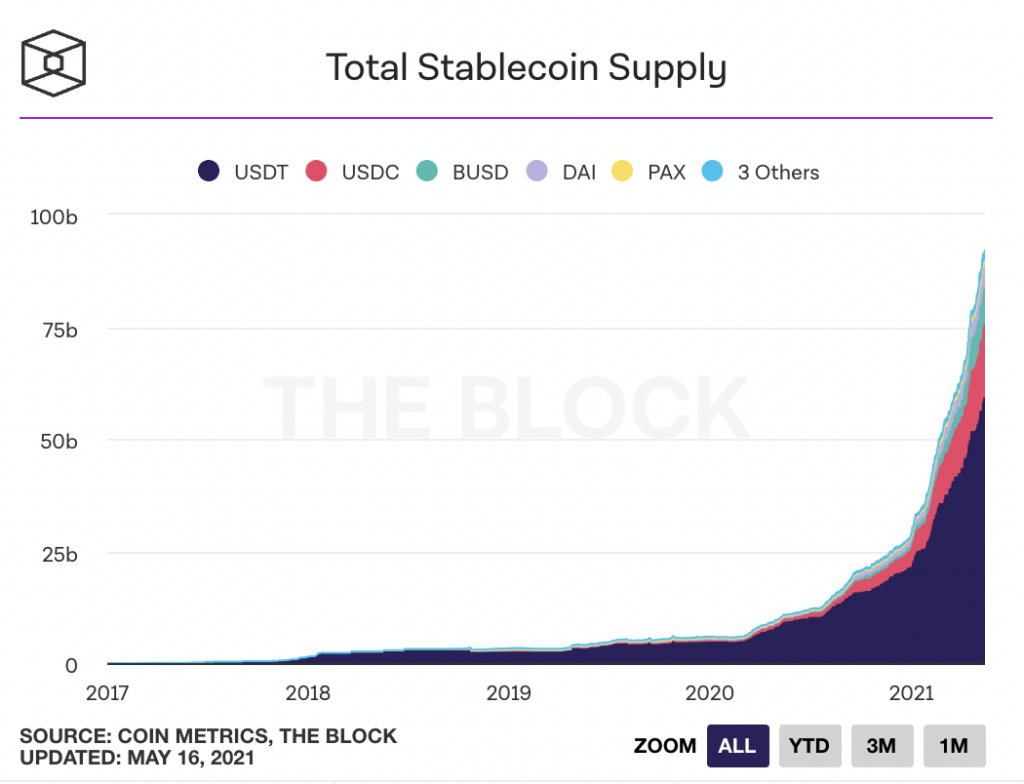
There are two types of stablecoins:
- Fiat-collateralized coins (e.g. Tether, USDC coin):
These stablecoins maintain reserves of equivalent value per minted coin (i.e. to mint a new Tether coin, Tether must keep $1 in their reserves). USD Coin $USDC ws is pegged to the U.S. dollar. It is the second-largest stablecoin by market capitalization. - Crypto-collateralized coins (e.g. DAI):
These stablecoins' value is pegged via smart protocols voted by DAOs (decentralized autonomous organizations). The biggest of these is MakerDAO, behind the DAI coin. It uses smart contract technology and Ethereum’s value to achieve the stability of the Dai token.
For example, Maker token holders can vote on the collateral ratio of various crypto assets to algorithmically peg the value of DAI to $1. If the collateral ratio of Ethereum is 200%, it means that to mint $100 of DAI, $200 worth of Ether must be deposited.
It’s like if a bank collateralized your house to get a loan, Maker does the same with your crypto assets. At 2:1, if the value dropped by over 50% your crypto position would be liquidated to cover the loan.
Stablecoins in crypto are a way to take advantage of crypto without the high risk of dealing with volatility.
DeFi Apps & Use Cases
Consider DeFi like you would the traditional financial system, which is not just about payments alone but about loans, savings, lending, insurance, trading, etc.
Anything you think of when you think of the financial industry is now being created on the blockchain. But unlike the traditional banking system of 9-5 hours, fees on top of fees, and endless paperwork — DeFi is the opposite.
It’s open 24/7, with no middleman, no central authority, and no paperwork. All transactions are visible on a permanent and public ledger.
Lending marketplaces on the blockchain make borrowing and lending cheaper, faster, and available to more people than the traditional systems.
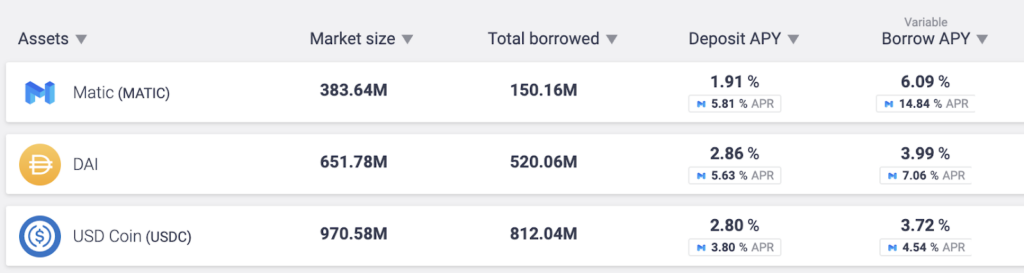
The most popular platforms for these are Compound.Finance, Maker Dao, & Aave. These projects let you borrow cryptocurrencies instantaneously (and often in large amounts) if you can prove you can pay back the loan.
For example, one of my most-used DeFi applications Aave currently manages over 17 Billion in assets. Aave enables the creation of money markets and users can earn interest on deposits and borrow assets.
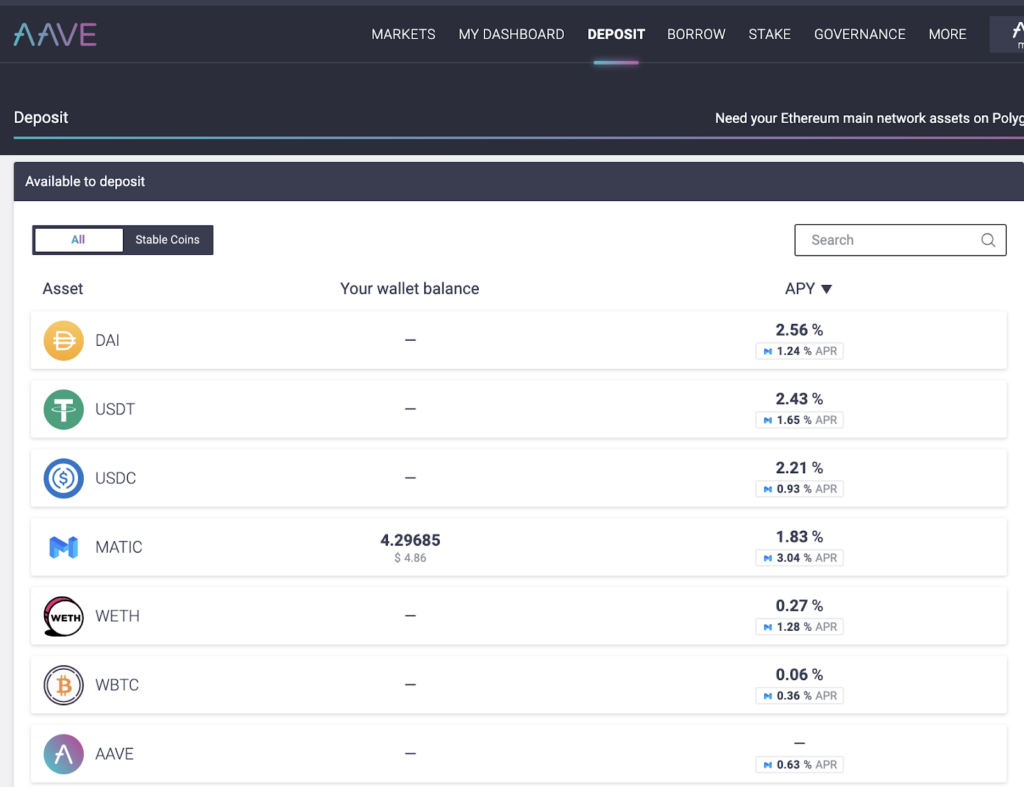
When you deposit into Aave you’ll be paid interest for storing your money there, at different APR per coin type. These rates are set algorithmically and will change day to day.
For example, the deposit rate today is 2.39%:

(I’ll get to what the 0.74% number is in a second)
Today the borrowing rate for the same asset is 3.61%:
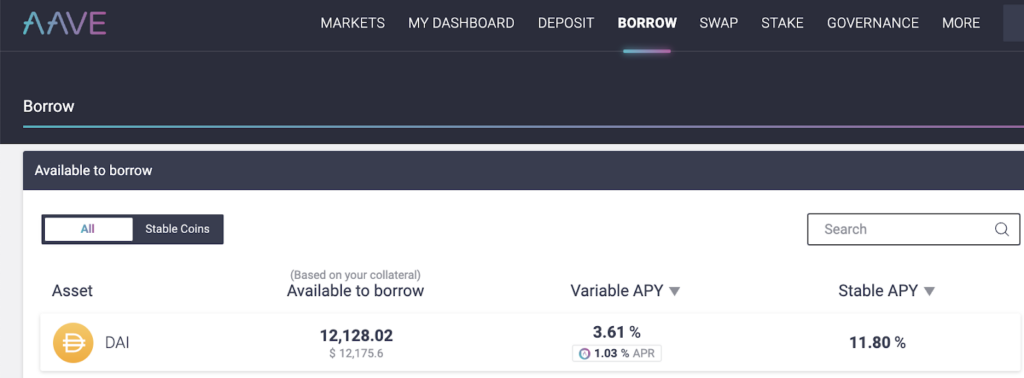
Aave makes money on transaction fees as well as the spread of the loan (so 1.42% in this instance).
Now to be able to borrow funds you have to have deposited collateral of which to borrow. You can then borrow up to 80% of the value you hold in there.
You could put $10,000 worth of ETH in there and then borrow $7,000 against it. You’ll make interest on the collateral and pay interest on what you borrowed.
What’s cool right now is that you also get a reward for using the platform! So in the above examples, you’ll make 0.74% on deposits paid out in the platform token (Aave), and 1.03% on money borrowed.
Why? Because these platforms are still in startup mode and want to attract depositors they offer rewards.
Remember in the early Uber days when you would get $10 for using the product and if you invited a friend you’d get more credit? This is similar, you’re getting rewarded for being an early user.
For example with the new sidechain Polygon, to incentive people to bring capital over there, they had big rewards available:
Yes, you could make more in rewards than you were borrowing
It’s like if you got a loan from a bank, and you were rewarded their company stock as a percentage of your loan. So in the above example of 4.5% APR for a loan, for every $100 you borrowed, you would receive $4.5 of stock.
You can then use these tokens to vote on proposals to upgrade the network or vote on new coins to be used as collateral. Or you can sell them for another coin.
The tokens for these platforms alone have increased in value a ton since they launched. See:
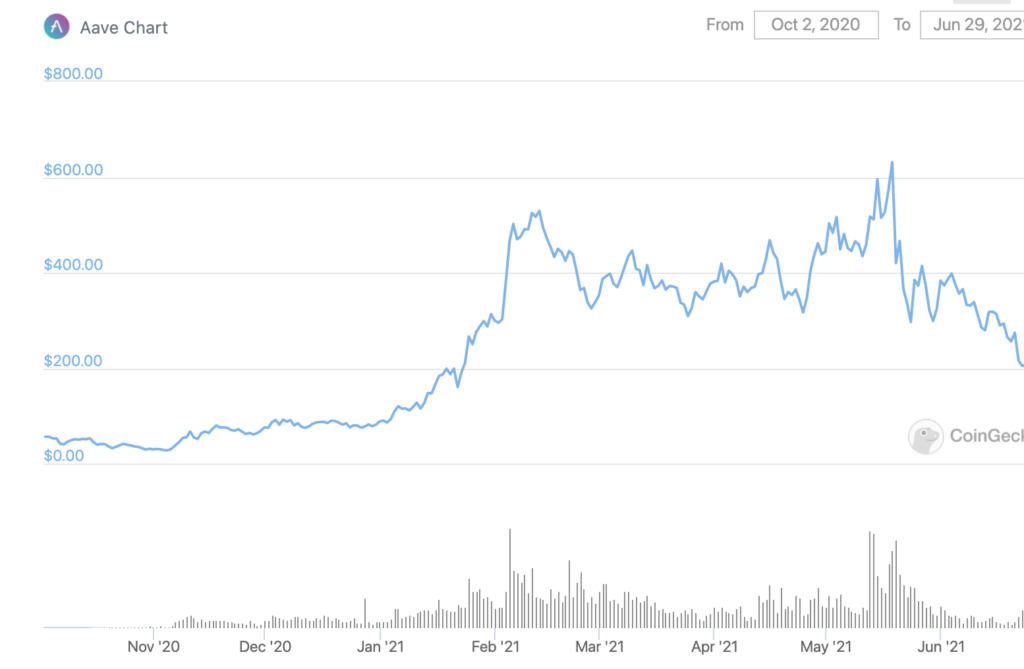
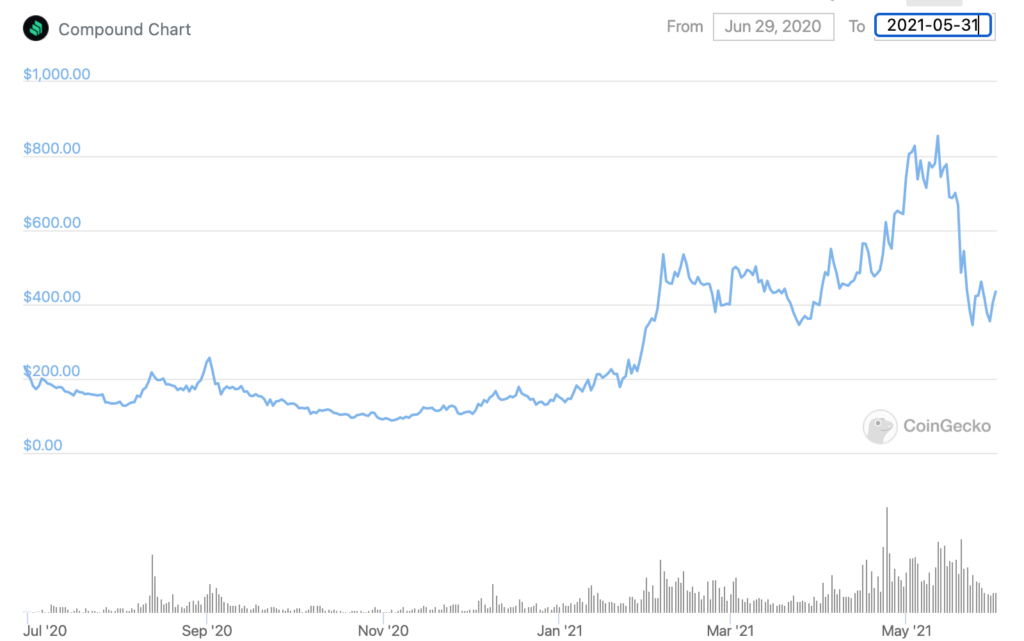
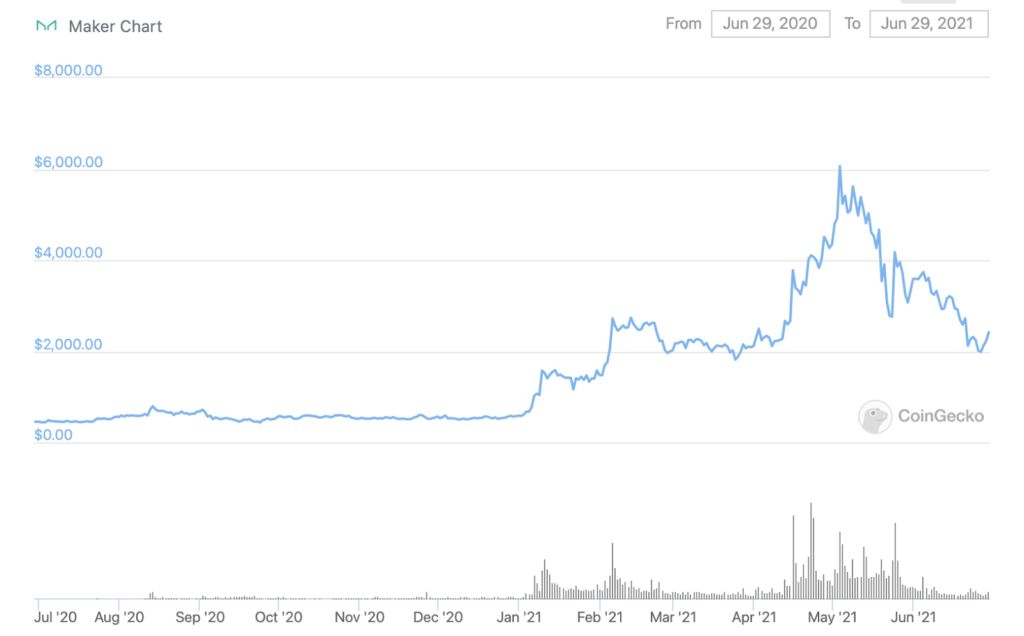
You can see here that there was a big correction in May as crypto markets dropped.
For everyone that was using a high percentage of leverage when the market crashed? Their risky behavior affected only themselves and they had their positions liquidated by the platforms to repay loans.
If this was TradFi, they would have run to Mommy and Daddy government to bail them out while executives collected bonus checks like we saw in 2008.
The May meltdown was the first real test these platforms had with a market crash and they handled it amazingly! Great post more about it here by my friend Nat. Here’s another great thread on how it went down:
Something to get your head around:
Head Line:
A major asset class crashed 42% in 14 days, wiping out $1.02trn in value in an orgy of liquidation of people up to 100 x levered, with very low regulation. Many tokens fell up to 70%, including unregulated lending and borrowing biz.— Raoul Pal (@RaoulGMI) May 25, 2021
Trading platform
An automated token exchange (AKA DEX; Decentralized Exchange) is a cryptocurrency exchange run entirely on smart contracts, letting you trade popular tokens directly from your wallet.
it’s like the trading app Robinhood, except it’s decentralized (they won’t stop you trading shitcoins when their Hedge Fund daddy gets mad).
The most popular Dexes are Uniswap and Sushi.
These are different from an exchange like Coinbase or Robinhood, which stores your crypto for you and holds your private keys for safekeeping. Sushi or Uniswap uses an innovative mechanism known as Automated Market Making to automatically settle trades near the market price.
Not only can you sell on the platform, but you can also provide liquidity by creating a pool and earning a share of exchange fees. More on this in a future article!
So how do you get started? The first thing you’ll need is crypto in your wallet.
Crypto wallets
One of the basic things to understand if you’re new to crypto is how your wallet works. Your wallet helps you manage the keys to your cryptocurrency. Keys are a fundamental part of cryptocurrency — when you own crypto, you own public and private keys that let you access your assets.
A crypto wallet is like your bank account, except it holds only your digital assets. It also allows you to both send and receive cryptocurrency to it.
There are two types of wallets:
Centralized
A third-party website system that keeps the coins on your behalf. While they keep your keys safe for you, they are a centralized system — meaning if there was a hack or government intervention you could lose access to your coins. Examples: Coinbase, Gemini, Robinhood
While cryptocurrencies themselves are very secure, exchanges can be affected by a variety of vulnerabilities, making them a prime target for malicious actors.
Decentralized
You control your wallet and are responsible for all your coins and the security of your keys. Examples: Ledger, Trezor, Metamask
If you have your crypto sitting in Coinbase, you really aren’t partaking in crypto. Not your keys, not your coins.
Coinbase, Kraken, Gemini — these are all on-ramps from the traditional system into crypto, but once you buy through them you can then transfer them out to your own wallet.
Software wallet
MetaMask acts as a wallet, but also a gateway to most crypto web apps. It allows you to interact with crypto and make use of decentralized tools and exchanges. For additional security, I would recommend also having a hardware wallet (a ledger or a Trezor) that is connected through MetaMask.
Hardware wallet
You want to connect a hardware wallet (like Ledger or Trezor) to your Metamask as an additional layer of protection.
This reduces the chance of a potential hack. You then confirm all transactions on your hardware wallet. If you lose your metamask password or the phrase, it doesn’t really matter as you can always set up a new account. Your assets are in your hardware wallet.

Without a hardware wallet attached, if your MetaMask is hacked someone can steal all your coins (my friend Nat just had this happen). They drained $30,000 from his wallet.
However, if you have a hardware wallet connected to that account they would need to be able to get access to that physical hardware wallet also.
Security
I recommend using one browser for only Crypto stuff (I use Brave). That means I only use this browser for crypto, if I’m working on anything business or personal I will use Chrome.
With your crypto browser, you want to have only the MetaMask extension installed. This is to ensure that there’s no bad actor or malware on another extension that could be used to get to your wallet!
You can never be too safe with your crypto!
To set up a wallet:
- Download Brave or whatever you want to use for your crypto-only browser
- Add MetaMask to your browser
- Save your seed phrase and keep it secure (this is the key to your coins) do not share with anyone!
- Here’s how to connect your hardware wallet
How to get started
If you’re reading this maybe you have money in Coinbase? Time to get off their platform (being decentralized is way cooler, trust me).
Don’t have crypto yet? I’d highly recommend Crypto.com (use this link and we both get $25) as it allows you to transfer to many different chains (avalanche, polygon, bsc, etc) so you can save on Ethereum gas fees which have gotten prohibitively expensive.
There’s also Coinbase as an option which you can transfer out from there. You’ll need ETH in your wallet to be able to make transactions though.
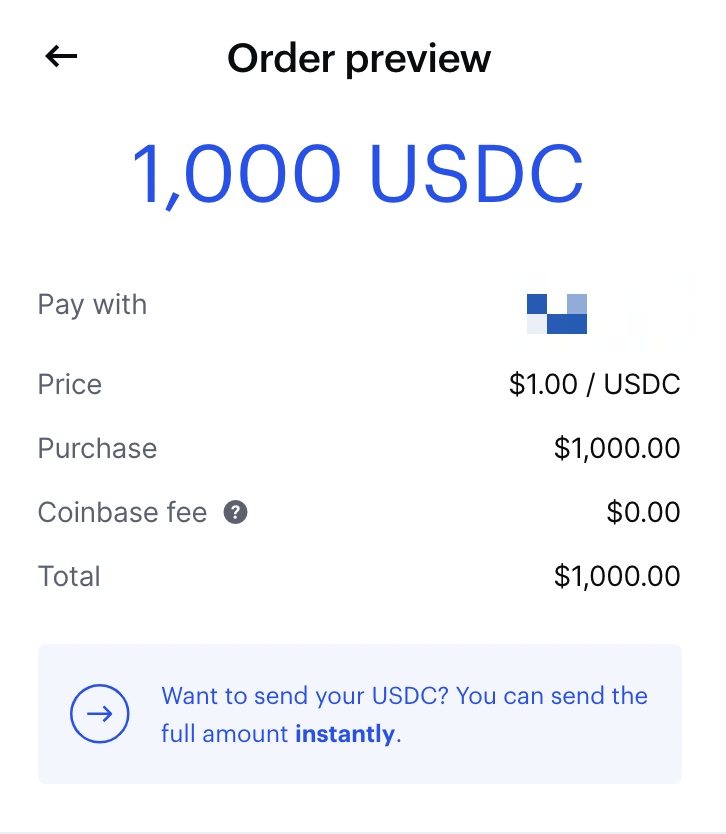
If you mainly want to stick with stablecoins you can buy USDC coin which has the lowest (if any fees):
Easy Mode Version
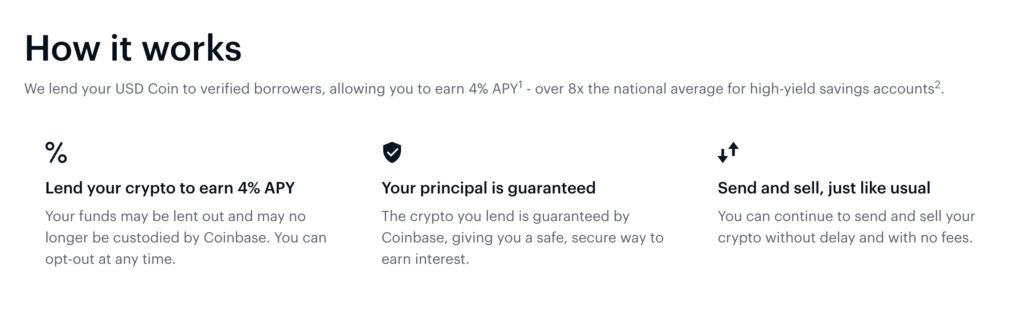
As of writing this Coinbase has opened up a 4% APR on USDC coin, so if all of this seems too daunting that’s the easy mode! Still over 10X what you would be getting in any other “high-yield” account. USDC coin is the safest stable coin as it’s fully collateralized. They will lend it out and guarantee your principle (not FDIC insured tho).
End note
Now I get that after reading about this the concept of wallets and security may seem daunting — however in my experience learning this is well worth it. We’re talking about asymmetric returns here, which yes has included me taking some risk.
Because of the complexity of wallets and setup, there is a barrier to entry that makes it not nearly as easy to start as it does swiping a few buttons on Coinbase. It’s a learning curve but it’s been the most fun thing I’ve been studying over the last year and will disrupt many industries in the future.
Over the last 12 months in DeFi, I’ve seen a lot already and have made all the n00b mistakes. For anyone interested in learning more I’ll be writing more on:
- What I’m buying and holding
- Sidechains & arbitrum
- Project rundowns
- Where I’m seeing the most return (w/ associated risk profiles)
- Tax and Crypto (but important)
If you want to learn about this sign up below (and I’ll share my DeFi toolkit with you)
Become a subscriber receive the latest updates in your inbox.





